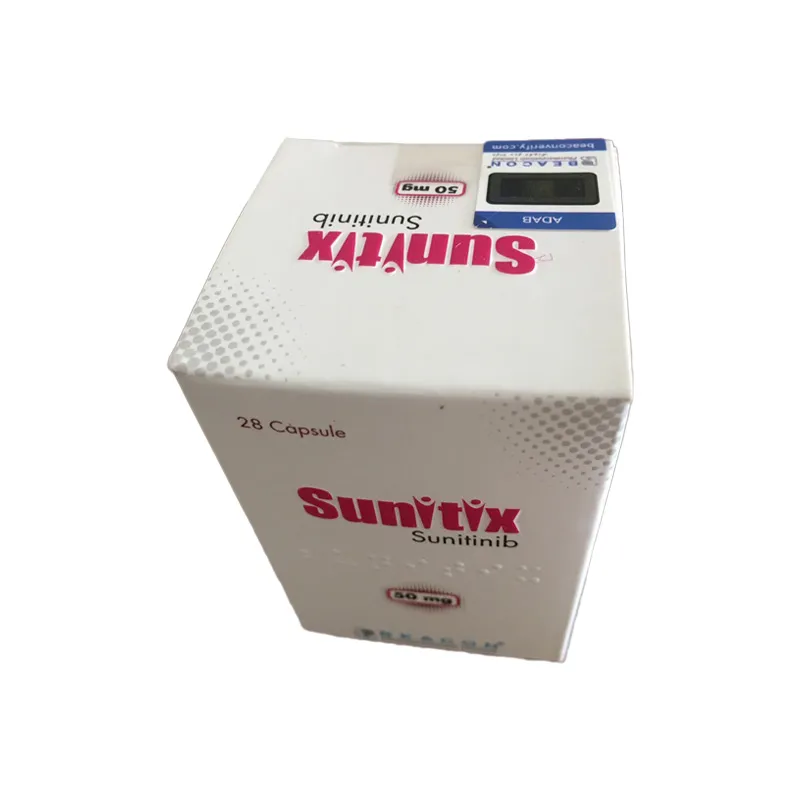
Buy Sunitix 50 Mg (Sunitinib)
Inquire NowTable of Contents
ToggleWhat is Sunitix 50 MG (Sunitinib)?
Sunitinib is used to treat gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST; a type of tumor that grows in the stomach, intestine (bowel), or esophagus (tube that connects the throat with the stomach) in people with tumors that were not treated successfully with imatinib or people who cannot take imatinib. Sunitinib is also used to treat advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC, a type of cancer that begins in the cells of the kidneys). Lenvanix 4 also use for renal cell carcinoma treatment.
Sunitinib is also used to help prevent the return of RCC in people who have RCC that has not spread and have had a kidney removed. Sunitinib is also used to treat pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET, a type of tumor that begins in certain cells of the pancreas) in people with tumors that have worsened and cannot be treated with surgery. Sunitinib is in a class of medications called kinase inhibitors. It works by blocking the action of the abnormal protein that signals cancer cells to multiply. This helps stop or slow the spread of cancer cells and may help shrink tumors. To know more about Sunitinib visit here.
Why should you buy the generic Sunitix 50 mg online?
First of all generic Sunitix is very affordable version of sunitinib for gastrointestinal stromal tumors or advanced renal cell carcinoma patients. It is a verified generic version of Sutent. Beacon pharmaceuticals Limited manufacture this generic version in Bangladesh. It is one of the renowned pharmaceutical companies who mostly made cancer medicine in Bangladesh.
After the Directorate General of Drug Administration of Bangladesh approves to manufacture sunitinib, they started to make it and sell it all over the world where generic medicine is allowed to use. It is the first generic version of Sutent which is selling regularly all over the world. It is also 90% cheaper than the brand version Which cost you less than 200 dollars.
COMPOSITION
Sunitix 50 Capsule: Each capsule contains Sunitinib Malate INN equivalent to Sunitinib 50 mg.
Sunitix 25 Capsule: Each capsule contains Sunitinib Malate INN equivalent to Sunitinib 25 mg.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY OF SUNITIX 50 MG
Sunitinib malate is a small molecule that inhibits multiple receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), some of which are implicated in tumor growth, pathologic angiogenesis and metastatic progression of cancer.
Pharmacokinetics in Special Populations
Population pharmacokinetic analyses of demographic data indicate that there are no clinically relevant effects of age, body weight, creatinine clearance, race, gender or ECOG score on the pharmacokinetics of Sunitinib or the primary active metabolite.
Pediatric Use: The pharmacokinetics of Sunitinib have not been evaluated in pediatric patients.
Renal Insufficiency: Sunitinib systemic exposure after a single dose of Sunitinib was similar in subjects with severe renal impairment (CLcr<30 mL/min) compared to subjects with normal renal function (CLcr>80 mL/min). Although Sunitinib was not eliminated through hemodialysis, the Sunitinib systemic exposure was 47% lower in subjects with ESRD on hemodialysis compared to subjects with normal renal function. Hepatic Insufficiency: Systemic exposures after a single dose of Sunitinib were similar in subjects with mild exocrine (Child-Pugh Class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) hepatic impairment compared to subjects with normal hepatic function.
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Sunitinib works by blocking multiple molecular targets implicated in the growth, proliferation and spread of cancer. Two important sunitinib targets, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) and platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) are expressed by many types of solid tumors and are thought to play a crucial role in angiogenesis, the process by which tumors acquire blood vessels, oxygen and nutrients needed for growth. Sunitinib also inhibits other targets important to tumor growth including KIT, FLT3 and RET.
INDICATIONS
Sunitix is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of:
⇒ Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) after disease progression on orintolerance to imatinib mesylate.
⇒ Advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
⇒ Progressive, well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (pNET) in patients with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
GIST and RCC: 50 mg orally once daily, with or without food, 4 weeks on treatment followed by 2 weeks off.
pNET: 37.5 mg orally once daily, with or without food, continuously without a scheduled off-treatment period.
Dose Modification: Dose interruptions and/or dose adjustments of 12.5 mg recommended based on individual safety and tolerability.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D
Sunitinib can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. As angiogenesis is a critical component of embryonic and fetal development, inhibition of angiogenesis following administration of Sunitinib should be expected to result in adverse effects on pregnancy. In animal reproductive studies in rats and rabbits, Sunitinib was teratogenic, embryotoxic and fetotoxic.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of Sunitinib in pregnant women. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to a fetus. Women of childbearing potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant while receiving treatment with sunitinib. Sunitinib was evaluated in pregnant rats (0.3, 1.5, 3.0, 5.0 mg/kg/day) and rabbits (0.5, 1, 5, 20 mg/kg/day) for effects on the embryo.
Significant increases in the incidence of embryolethality and structural abnormalities were observed in rats at the dose of 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 5.5 times the systemic exposure [combined AUC of Sunitinib + primary active metabolite] in patients administered the recommended daily doses [RDD]). Significantly increased embryolethality was observed in rabbits at 5 mg/kg/day while developmental effects were observed at >_1 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.3 times the AUC in patients administered the RDD of 50mg/day).
Developmental effects consisted of fetal skeletal malformations of the ribs and vertebrae in rats. In rabbits, cleft lip was observed at 1 mg/kg/day and cleft lip and cleft palate were observed at 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 2.7 times the AUC in patients administered the RDD). Neither fetal loss nor malformations were observed in rats dosed at 3 mg/kg/day (approximately 2.3 times the AUC in patients administered the RDD). Sunitinib (0.3, 1.0, 3.0 mg/kg/day) was evaluated in a pre- and postnatal development study in pregnant rats.
Maternal body weight gains were reduced during gestation and lactation at doses >_1 mg/kg/day but no maternal reproductive toxicity was observed at doses up to >_3 mg/kg/day (approximately 2.3 times the AUC in patients administered the RDD). At the high dose of 3 mg/kg/day, reduced body weights were observed at birth and persisted for offspring of both sexes during the pre-weaning period and in males during post-weaning period. No other developmental toxicity was observed at doses up to 3 mg/kg/day (approximately 2.3 times the AUC in patients administered the RDD).
Nursing Mothers
Sunitinib and its metabolites are excreted in rat milk. In lactating female rats administered 15 mg/kg, Sunitinib and its metabolites were extensively excreted in milk at concentrations up to 12-fold higher than in plasma. It is not known whether this drug or its primary active metabolite are excreted in human milk.
Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Sunitinib, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of Sunitinib in pediatric patients have not been established. Physeal dysplasia was observed in cynomolgus monkeys with open growth plates treated for >_ 3 months (3 month dosing 2, 6, 12 mg/kg/day; 8 cycles of dosing 0.3, 1.5, 6.0 mg/kg/day) with Sunitinib at doses that were > 0.4 times the RDD based on systemic exposure (AUC). In developing rats treated continuously for 3 months (1.5, 5.0 and 15.0 mg/kg) or 5 cycles (0.3, 1.5, and 6.0 mg/kg/day), bone abnormalities consisted of thickening of the epiphyseal cartilage of the femur and an increase of fracture of the tibia at doses >_ 5 mg/kg (approximately 10 times the RDD based on AUC).
Additionally, caries of the teeth were observed in rats at >5 mg/kg. The incidence and severity of physeal dysplasia were dose-related and were reversible upon cessation of treatment; however, findings in the teeth were not. A no effect level was not observed in monkeys treated continuously for 3 months, but was 1.5 mg/kg/day when treated intermittently for 8 cycles. In rats the no effect level in bones was <_ 2 mg/kg/day.
Geriatric Use
Of 825 GIST and RCC patients who received Sunitinib on clinical studies, 277 (34%) were 65 and over. In the Phase 3 pNET study, 22 (27%) patients who received Sunitinib were 65 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between younger and older patients.
Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment to the starting dose is required when administering Sunitinib to patients with Child-Pugh Class A or B hepatic impairment. Sunitinib and its primary metabolite are primarily metabolized by the liver. Systemic exposures after a single dose of Sunitinib were similar in subjects with mild or moderate (Child-Pugh Class A and B) hepatic impairment compared to subjects with normal hepatic function.
Sunitinib was not studied in subjects with severe (Child-Pugh Class C) hepatic impairment. Studies in cancer patients have excluded patients with ALT or AST >2.5 x ULN or, if due to liver metastases, >5.0 x ULN.
Renal Impairment
No adjustment to the starting dose is required when administering Sunitinib to patients with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment. Subsequent dose modifications should be based on safety and tolerability. In patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) on hemodialysis, no adjustment to the starting dose is required. However, compared to subjects with normal renal function, the Sunitinib exposure is 47% lower in subjects with ESRD on hemodialysis.
OVERDOSAGE
Treatment of overdose with Sunitinib should consist of general supportive measures. There is no specific antidote for overdosage with Sunitinib. If indicated, elimination of unabsorbed drug should be achieved by emesis or gastric lavage. A few cases of accidental overdose have been reported; these cases were associated with adverse reactions consistent with the known safety profile of Sunitinib or without adverse reactions. A case of intentional overdose involving the ingestion of 1,500 mg of Sunitinib in an attempted suicide was reported without adverse reaction.
In non clinical studies mortality was observed following as few as 5 daily doses of 500 mg/kg (3000 mg/m2 ) in rats. At this dose, signs of toxicity included impaired muscle coordination, head shakes, hypoactivity, ocular discharge, piloerection and gastrointestinal distress. Mortality and similar signs of toxicity were observed at lower doses when administered for longer durations.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None
PRECAUTIONS
Hepatotoxicity, including liver failure has been observed. Monitor liver function tests before initiation of treatment during each cycle of treatment, and as clinically indicated. Sunitinib should be interrupted for Grade 3 or 4 drug-related hepatic adverse events and discontinued if there is no resolution. Do not restart Sunitinib if patients subsequently experience severe changes in liver function tests or have other signs and symptoms of liver failure.
Women of childbearing potential should be advised of the potential hazard to the fetus and to avoid becoming pregnant. Cardiac toxicity including left ventricular ejection fraction declines to below the lower limit of normal and cardiac failure including death have occurred. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure.
Prolonged QT intervals and Torsade de Pointes have been observed. Use with caution in patients at higher risk for developing QT interval prolongation. When using Sunitinib, monitoring with on treatment electrocardiograms and electrolytes should be considered.
Hypertension may occur. Monitor blood pressure and treat as needed. Hemorrhagic events including tumor-related hemorrhage have occurred. Perform serial complete blood counts and physical examinations. Osteonecrosis of the jaw has been reported. Consider preventive dentistry prior to treatment with Sunitinib. If possible, avoid invasive dental procedures, particularly in patients receiving intravenous bisphosphonate therapy.
Cases of Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS) have been reported primarily in patients with RCC and GIST with high tumor burden. Monitor these patients closely and treat as clinically indicated. Thyroid dysfunction may occur. Patients with signs and/or symptoms suggestive of hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism should have laboratory monitoring of thyroid function performed and be treated as per standard medical practice.
Temporary interruption of therapy with Sunitinib is recommended in patients undergoing major surgical procedures. Adrenal hemorrhage was observed in animal studies. Monitor adrenal function in case of stress such as surgery, trauma or severe infection.
ADVERSE EFFECTS
The most common adverse reactions (>_20%) are fatigue, asthenia, fever, diarrhea, nausea, mucositis/stomatitis, vomiting, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, constipation, hypertension, peripheral edema, rash, hand-foot syndrome, skin discoloration, dry skin, hair color changes, altered taste, headache, back pain, arthralgia, extremity pain, cough, dyspnea, anorexia and bleeding.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Consider dose reduction of Sunitinib when administered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
CYP3A4 Inducers: Consider dose increase of Sunitinib when administered with CYP3A4 inducers.
PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION
Storage condition
Store in a cool and dry place, away from light. Keep out of the reach of children.
Presentation & Packing
Sunitix 50 Capsule: Each commercial box contains 28 Capsules in a bottle.
Sunitix 25 Capsule: Each commercial box contains 28 Capsules in a bottle.
Buy Sunitix 50 Mg Online
Are you interested to buy Sunitix 50 mg online? or you need 25 mg version? Don’t worry. 100 Meds can help you to find reliable and verified medicine at affordable cost. Please contact our support team by using email, whatsapp or wechat. Even you can contact our facebook page.
You must be logged in to post a review.





Reviews
There are no reviews yet.