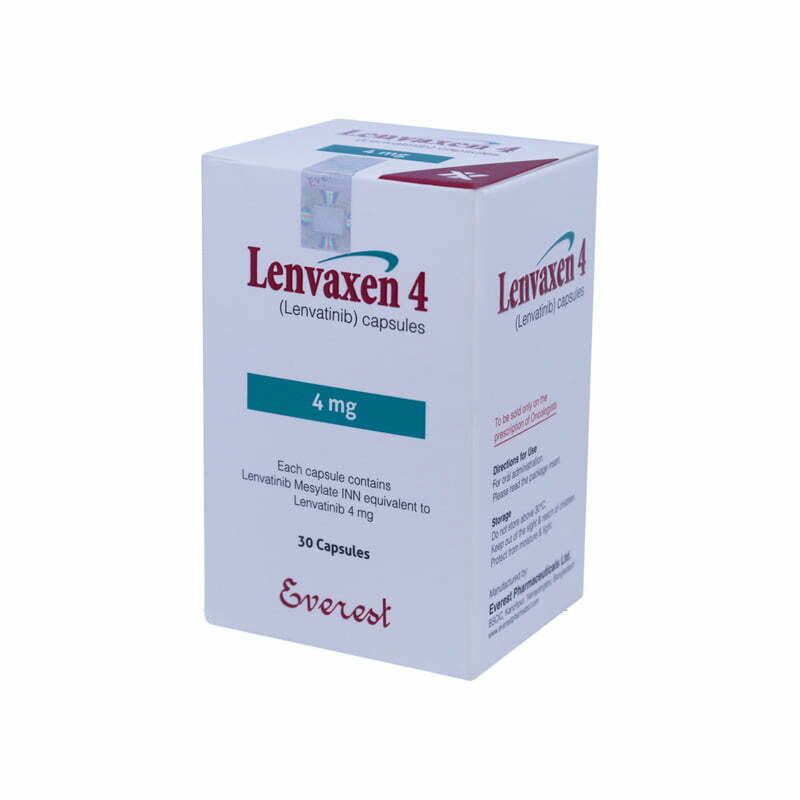
Buy Lenvaxen (Lenvatinib) Online
Inquire NowTable of Contents
ToggleWhat is Lenvaxen (Lenvatinib)?
Lenvaxen (Lenvatinib) is used to treat a certain type of thyroid cancer that has returned or that has spread to other parts of the body and cannot be treated with radioactive iodine. Lenvatinib is also used along with everolimus to treat renal cell carcinoma (RCC, a type of cancer that begins in the kidney) in people who have previously received treatment with another chemotherapy medication.
Lenvatinib is also used along with pembrolizumab as an initial treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Lenvatinib is also used to treat hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC; a type of liver cancer) that cannot be treated with surgery.
Lenvatinib is also used along with pembrolizumab to treat a certain type of cancer of the endometrium (lining of the uterus) that has spread to other parts of the body or worsened during or after treatment with chemotherapy medications or that cannot be treated with surgery or radiation therapy. Lenvatinib is in a class of medications called kinase inhibitors. It works by blocking the action of an abnormal protein that signals cancer cells to multiply. This helps stop the spread of cancer cells. Source: MedlinePlus.
Why should you buy the generic Lenvaxen online?
First of all generic lenvaxen is very affordable version of lenvatinib for thyroid cancer patients. It is a verified generic version of Lenvima. Everest pharmaceuticals Limited manufacture this generic version in Bangladesh. It is one of the renowned pharmaceutical companies who mostly made cancer medicine in Bangladesh. After the Directorate General of Drug Administration of Bangladesh approves to manufacture lenvatinib, they started to make it and sell it all over the world where generic medicine is allowed to use.
It is the 2nd generic version of Lenvima which is selling regularly all over the world. It is also 97% cheaper than the brand version of lenvatinib. Which cost you less than 200 dollars for 4 mg version.
COMPOSITION
LENVAXEN 4 capsules: Each capsule contains Lenvatinib Mesylate INN equivalent to Lenvatinib 4 mg.
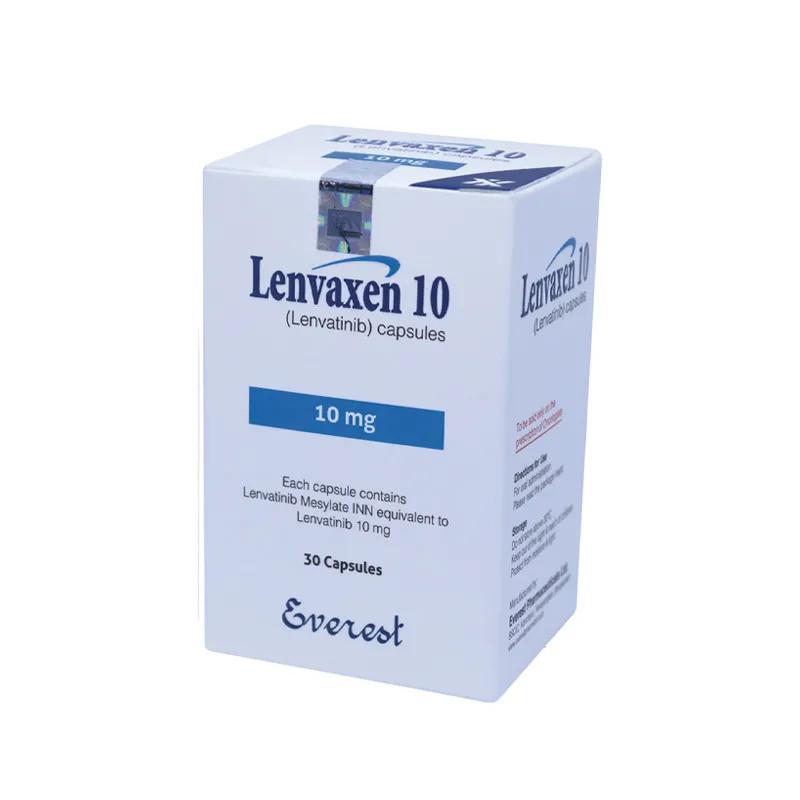
LENVAXEN 10 capsules: Each capsule contains Lenvatinib Mesylate INN equivalent to Lenvatinib 10 mg.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE OF LENVAXEN
Lenvatinib is indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with progressive, locally advanced or metastatic, differentiated (papillary/follicular/Hurthle cell) thyroid carcinoma (DTC), refractory to radioactive iodine (RAI).
Lenvatinib is indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with advanced or unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who have received no prior systemic therapy.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended Dosage for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer (DTC)
The recommended dosage of lenvatinib is 24 mg orally once daily until disease progression or until unacceptable toxicity.
Recommended Dosage for Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) The recommended dosage of lenvatinib is 18 mg in combination with 5 mg everolimus orally once daily until disease progression or until unacceptable toxicity.
Refer to everolimus prescribing information for recommended everolimus dosing information.
Recommended Dosage for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
The recommended dosage of lenvatinib is based on actual body weight, 12 mg for patients greater than or equal to 60 kg or 8 mg for patients less than 60 kg. Take lenvatinib orally once daily until disease progression or until unacceptable toxicity.
Reduce the dose for certain patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Take lenvatinib once daily, with or without food, at the same time each day. If a dose is missed and cannot be taken within 12 hours, skip that dose and take the next dose at the usual time of administration.
DOSAGE MODIFICATION
Management of some adverse reactions may require dose interruption, adjustment, or discontinuation of lenvatinib therapy. Mild to moderate adverse reactions (e.g., Grade 1 or 2) generally do not warrant interruption of lenvatinib, unless intolerable to the patient despite optimal management. Details for monitoring, dose adjustment and discontinuation are provided in Table 1 & 2.
Table 1 Dose modifications from recommended lenvatinib daily dose in DTC patientsa
Dose level | Daily dose | Number of capsules |
Recommended daily dose | 24 mg orally once daily | Two 10 mg capsules plus one 4 mg capsule |
First dose reduction | 20 mg orally once daily | Two 10 mg capsules |
Second dose reduction | 14 mg orally once daily | One 10 mg capsule plus one 4 mg capsule |
Third dose reduction | 10 mg orally once dailya | One 10 mg capsule |
a: Further dose reductions should be considered on an individual patient basis as limited data are available for doses below 10 mg. | ||
Table 2 Dose modifications from recommended lenvatinib daily dose in HCC patients
Starting Dose | AO kg BW 12 mg (three 4 mg capsules orally once daily) | <60 kg BW 8 mg (two 4 mg capsules orally once daily) | |
Persistent and Intolerable Grade 2 or Grade 3 Toxicitiesa | |||
Adverse Reaction | Modification | Adjusted Dose (AO kg BW) | Adjusted Dose (<60 kg BW) |
First occurrence | Interrupt until resolved to Grade 0-1 or baselined | 8 mg (two 4 mg capsules) orally once daily | 4 mg (one 4 mg capsule) orally once daily |
Second occurrence (same reaction or new reaction) | Interrupt until resolved to Grade 0-1 or baselined | 4 mg (one 4 mg capsule) orally once daily | 4 mg (one 4 mg capsule) orally every other day |
Third occurrence (same reaction or new reaction) | Interrupt until resolved to Grade 0-1 or baselined | 4 mg (one 4 mg capsule) orally every other day | Discontinue |
Life-threatening toxicities (Grade 4): Discontinue’ | |||
| |||
CONTRAINDICATION
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypertension
Hypertension has been reported in patients treated with lenvatinib, usually occurring early in the course of treatment. Blood pressure (BP) should be well controlled prior to treatment with lenvatinib and if patients are known to be hypertensive, they should be on a stable dose of antihypertensive therapy for at least 1 week prior to treatment with lenvatinib. Serious complications of poorly controlled hypertension, including aortic dissection, have been reported.
The early detection and effective management of hypertension are important to minimise the need for lenvatinib dose interruptions and reductions. Antihypertensive agents should be started as soon as elevated BP is confirmed. BP should be monitored after 1 week of treatment with lenvatinib, then every 2 weeks for the first 2 months, and monthly thereafter.
Cardiac Dysfunction
Serious and fatal cardiac dysfunction can occur with lenvatinib. Across clinical trials in 799 patients with DTC, RCC or HCC, Grade 3 or higher cardiac dysfunction (including cardiomyopathy, left or right ventricular dysfunction, congestive heart failure, cardiac failure, ventricular hypokinesia, or decrease in left or right ventricular ejection fraction of more than 20% from baseline) occurred in 3% of lenvatinib-treated patients. Monitor patients for clinical symptoms or signs of cardiac dysfunction. Withhold and resume at a reduced dose upon recovery or permanently discontinue lenvatinib based on severity.
Arterial Thromboembolic Events
Among patients receiving lenvatinib or lenvatinib with everolimus, arterial thromboembolic events of any severity occurred in 2% of patients in Study 205 (RCC), 2% of patients in REFLECT (HCC) and 5% of patients in SELECT (DTC). Grade 3 to 5 arterial thromboembolic events ranged from 2% to 3% across all clinical trials. Permanently discontinue lenvatinib following an arterial thrombotic event.
The safety of resuming lenvatinib after an arterial thromboembolic event has not been established and lenvatinib has not been studied in patients who have had an arterial thromboembolic event within the previous 6 months.
Hepatotoxicity
Across clinical studies enrolling 1327 lenvatinib-treated patients with malignancies other than HCC, serious hepatic adverse reactions occurred in 1.4% of patients. Fatal events, including hepatic failure, acute hepatitis and hepatorenal syndrome, occurred in 0.5% of patients. In REFLECT (HCC), hepatic encephalopathy (including hepatic encephalopathy, encephalopathy, metabolic encephalopathy, and hepatic coma) occurred in 8% of lenvatinib-treated patients and 3% of sorafenib-treated patients.
Grade 3 to 5 hepatic encephalopathy occurred in 5% of lenvatinib-treated patients and 2% of sorafenib-treated patients. Grade 3 to 5 hepatic failure occurred in 3% of lenvatinib-treated patients and 3% of sorafenib-treated patients.
Two percent of patients discontinued lenvatinib and 0.2% discontinued sorafenib due to hepatic encephalopathy and 1% of patients discontinued lenvatinib or sorafenib due to hepatic failure. Monitor liver function prior to initiating lenvatinib, then every 2 weeks for the first 2 months, and at least monthly thereafter during treatment.
Renal Failure or Impairment
Serious including fatal renal failure or impairment can occur with lenvatinib. Renal impairment occurred in 14% of patients receiving lenvatinib in SELECT (DTC) and in 7% of patients receiving lenvatinib in REFLECT (HCC). Grade 3 to 5 renal failure or impairment occurred in 3% (DTC) and 2% (HCC) of patients, including 1 fatality in each study. In Study 205 (RCC), renal impairment or renal failure occurred in 18% of patients receiving lenvatinib with everolimus, including Grade 3 in 10% of patients.
Initiate prompt management of diarrhea or dehydration/hypovolemia. Withhold and resume at a reduced dose upon recovery or permanently discontinue lenvatinib for renal failure or impairment based on severity.
SIDE EFFECTS
Hypertension, Cardiac Dysfunction, Arterial Thromboembolic Events, Hepatotoxicity, Renal Failure and Impairment Proteinuria, Diarrhea, Fistula Formation and Gastrointestinal Perforation, QT Interval Prolongation, Hypocalcemia, Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome Hemorrhagic Events, Impairment of Thyroid Stimulating Hormone Suppression/Thyroid Dysfunction, Wound Healing Complications.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Chemotherapeutic agents
Concomitant administration of lenvatinib, carboplatin, and paclitaxel has no significant impact on the pharmacokinetics of any of these 3 substances.
Effect of Lenvatinib on other medicine
A clinical drug-drug interaction (DDI) study in cancer patients showed that plasma concentrations of midazolam (a sensitive CYP3A and Pgp substrate) were not altered in the presence of lenvatinib. No significant drug-drug interaction is therefore expected between lenvatinib and other CYP3A4/Pgp substrates.
Oral contraceptives
It is currently unknown whether lenvatinib may reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives, and therefore women using oral hormonal contraceptives should add a barrier method.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATION
Women of childbearing potential
Women of childbearing potential should avoid becoming pregnant and use highly effective contraception while on treatment with lenvatinib and for at least one month after finishing treatment. It is currently unknown whether lenvatinib may reduce the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives, and therefore women using oral hormonal contraceptives should add a barrier method.
Pregnancy
There are no data on the use of lenvatinib in pregnant women. Lenvatinib was embryotoxic and teratogenic when administered to rats and rabbits. Lenvatinib should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary and after a careful consideration of the needs of the mother and the risk to the foetus.
Breast-feeding
It is not known whether lenvatinib is excreted in human milk. Lenvatinib and its metabolites are excreted in rat milk. A risk to newborns or infants cannot be excluded and, therefore, lenvatinib is contraindicated during breast-feeding.
Fertility
Effects in humans are unknown. However, testicular and ovarian toxicity has been observed in rats, dogs, and monkeys.
Patients with Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of lenvatinib following a single 24 mg dose were evaluated in subjects with mild (CLcr 60-89 mL/min), moderate (CLcr 30-59 mL/min), or severe (CLcr <30 mL/min) renal impairment, and compared to healthy subjects. Subjects with end stage renal disease were not studied. The AUC(o-ins) for subjects with renal impairment were similar compared to those for healthy subjects.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of lenvatinib following a single 10 mg dose were evaluated in subjects with mild (Child-Pugh A) or moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment. The pharmacokinetics of a single 5 mg dose were evaluated in subjects with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment. Compared to subjects with normal hepatic function, the dose-adjusted AUC(o-int) of lenvatinib for subjects with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment were 119%, 107%, and 180%, respectively. Apparent oral clearance of lenvatinib in patients with HCC and mild hepatic impairment was similar to patients with HCC and moderate hepatic impairment.
Paediatric Population
Paediatric patients have not been studied.
OVERDOSE
The highest doses of lenvatinib studied clinically were 32 mg and 40 mg per day. Accidental medication errors resulting in single doses of 40 to 48 mg have occurred in clinical trials. The most frequently observed adverse drug reactions at these doses were hypertension, nausea, diarrhoea, fatigue, stomatitis, proteinuria, headache, and aggravation of PPE. There have also been reports of overdose with lenvatinib involving single administrations of 6 to 10 times the recommended daily dose.
These cases were associated with adverse reactions consistent with the known safety profile of lenvatinib (i.e., renal and cardiac failure), or were without adverse reactions.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Lenvatinib is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor that selectively inhibits the kinase activities of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors VEGFR1 (FLT1), VEGFR2 (KDR), and VEGFR3 (FLT4), in addition to other proangiogenic and oncogenic pathway-related RTKs including fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptors FGFR1, 2, 3, and 4, the platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor PDGFRa, KIT, and RET.
In addition, lenvatinib had selective, direct antiproliferative activity in hepatocellular cell lines dependent on activated FGFR signalling, which is attributed to the inhibition of FGFR signalling by lenvatinib.
Although not studied directly with lenvatinib, the mechanism of action (MOA) for hypertension is postulated to be mediated by the inhibition of VEGFR2 in vascular endothelial cells. Similarly, although not studied directly, the MOA for proteinuria is postulated to be mediated by downregulation of VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 in the podocytes of the glomerulus.
The mechanism of action for hypothyroidism is not fully elucidated.
Pharmacokinetic properties
Pharmacokinetic parameters of lenvatinib have been studied in healthy adult subjects, adult subjects with hepatic impairment, renal impairment, and solid tumours.
Absorption
Lenvatinib is rapidly absorbed after oral administration with T. typically observed from 1 to 4 hours postdose. Food does not affect the extent of absorption but slows the rate of absorption. When administered with food to healthy subjects, peak plasma concentrations are delayed by 2 hours. Absolute bioavailability has not been determined in humans; however, data from a mass-balance study suggest that it is in the order of 85%. Lenvatinib exhibited good oral bioavailability in dogs (70.4%) and monkeys (78.4%).
Distribution
In vitro binding of lenvatinib to human plasma proteins is high and ranged from 98% to 99% (0.3 – 30 pg/mL, mesylate). This binding was mainly to albumin with minor binding to a1-acid glycoprotein and y-globulin.
In vitro, the lenvatinib blood-to-plasma concentration ratio ranged from 0.589 to 0.608 (0.1 — 10 pg/mL, mesylate). Lenvatinib is a substrate for P-gp and BCRP. Lenvatinib is not a substrate for OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, OCT2, MATE1, MATE2-K or the bile salt export pump BSEP.
In patients, the median apparent volume of distribution (Vz/F) of the first dose ranged from 50.5 L to 92 L and was generally consistent across the dose groups from 3.2 mg to 32 mg. The analogous median apparent volume of distribution at steady-state (Vz/Fss) was also generally consistent and ranged from 43.2 L to 121 L.
PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION
Storage Conditions
Store in a cool and dry place. Do not store above 30°C. Do not take lenvatinib if it is suspected of having been exposed to temperatures greater than 40° C or 104° F.
Keep the bottle out of reach and sight of the children. Dispended only in original container.
HOW SUPPLIED
LENVAXEN 4 capsules: Each Child-resistant HDPE container contains 30 capsules (each capsule contains Lenvatinib Mesylate INN equivalent to Lenvatinib 4 mg).
LENVAXEN 10 capsules: Each Child-resistant HDPE container contains 30 capsules (each capsule contains Lenvatinib Mesylate INN equivalent to Lenvatinib 10 mg).
Buy Lenvaxen Online
Are you interested to purchase Lenvaxen online? Don’t worry. 100 Meds can help you to find reliable and verified medicine at affordable cost. Please contact our support team by using email, whatsapp or wechat. Even you can contact our facebook page.
You must be logged in to post a review.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.