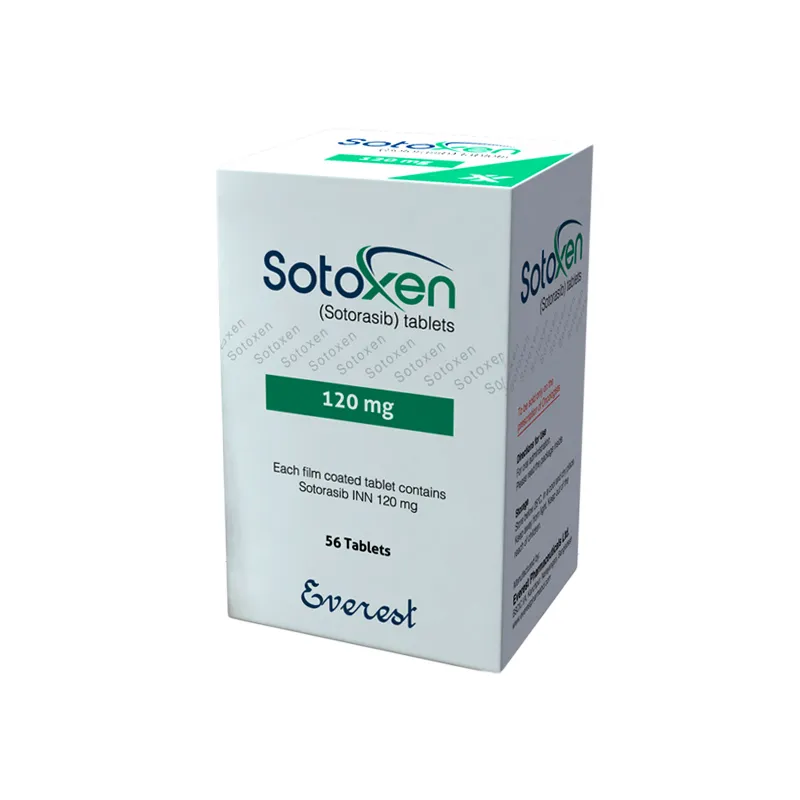
Buy Generic Sotorasib Online
Inquire NowTable of Contents
ToggleWhy is Sotorasib prescribed?
Why should you buy the generic Sotorasib online?
First of all generic Sotoxen is very affordable version of sotorasib for non-small-cell lung carcinomas patients. It is a verified generic version of Lumakras. Everest pharmaceuticals Limited manufacture this generic version in Bangladesh. It is one of the renowned pharmaceutical companies who mostly made cancer medicine in Bangladesh. After the Directorate General of Drug Administration of Bangladesh approves to manufacture sotorasib, they started to make it and sell it all over the world where generic medicine is allowed to use.
It is the first generic version of Lumakras which is selling regularly all over the world. It is also 75% cheaper than the brand version of sotorasib. Which cost you less than 1000 dollars. There are some more medicine available for NSCLC patients. Osimertinib is one of them. To know more you can visit our shop page.
COMPOSITION
SOTOXEN tablet: Each film-coated tablet contains Sotorasib INN 120 mg.
PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action:
Sotorasib is a potent and highly selective KRASG12C (Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog) inhibitor, which covalently and irreversibly binds to the unique cysteine of KRASG12C. Inactivation of KRASG12C by Sotorasib blocks tumour cell signalling and survival, inhibits cell growth, and promotes apoptosis selectively in tumours harbouring KRASG12C, an oncogenic driver of tumourigenesis across multiple cancer types. The potency and selectivity of Sotorasib is enhanced through the unique binding to both the P2 pocket and the His95 surface groove, locking the protein in an inactive state that prevents downstream signalling, without affecting wild-type KRAS.
Sotorasib demonstrated in vitro and in vivo inhibition of KRASG12C with minimal detectable off-target activity against other cellular proteins and processes. Sotorasib impaired oncogenic signalling and tumour cell survival at clinically relevant exposures in numerous pre-clinical models expressing KRASG12C. Sotorasib also enhanced antigen presentation and inflammatory cytokine production only in tumour cells with KRASG12C. Sotorasib induced anti-tumour inflammatory responses and immunity, driving permanent and complete tumour regressions in immunocompetent mice implanted with KRASG12C expressing tumours.
Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption
Following an oral, single-dose administration, Sotorasib was absorbed with median time to achieve peak concentration of 1 hour.
Effect of food
Following administration of Sotorasib with a high-fat, high-calorie meal, there was no effect on Cmax, and AUC increased by 38% compared to administration under fasted conditions. Sotorasib can be administered with or without food.
Distribution
The mean volume of distribution at steady state of Sotorasib was 211 L. In vitro, plasma protein binding of Sotorasib was 89%.
Biotransformation
The main metabolic pathways of Sotorasib were conjugation and oxidative metabolism.
Elimination
At 960 mg once daily, the steady state apparent clearance is 26.2 L/hir. The mean half-life is 5 hours. Steady state was reached within 22 days and remained stable. No accumulation with multiple dosing was observed. Sotorasib is primarily eliminated in faces, with approximately 74% of the dose recovered in faces and 6% (1% unchanged) recovered in urine.
Pharmacokinetics in special populations
No clinically meaningful differences in the pharmacokinetics of Sotorasib were observed based on age, sex, race or ethnicity, body weight, line of therapy, ECOG PS, mild renal impairment (CrCL: ≥ 60 mL/min), or mild hepatic impairment (AST or ALT < 2.5 x ULN or total bilirubin < 1.5 x ULN). The effect of moderate to severe renal or hepatic impairment on Sotorasib pharmacokinetics has not been studied.
INDICATION AND USAGE OF SOTORASIB
Sotorasib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with KRAS G12C-mutated locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), as determined by an FDA-approved test, who have received at least one prior systemic therapy.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage of Sotorasib is 960 mg (eight 120 mg tablets) orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Take Sotorasib at the same time each day with or without food. Swallow tablets whole. Do not chew, crush or split tablets. If a dose of Sotorasib is missed by more than 6 hours, take the next dose as prescribed the next day. Do not take 2 doses at the same time to make up for the missed dose.
If vomiting occurs after taking Sotorasib, do not take an additional dose. Take the next dose as prescribed the next day.
CONTRAINDICATION
None.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hepatotoxicity
Sotorasib can cause hepatotoxicity, which may lead to drug-induced liver injury and hepatitis. Among 357 patients who received Sotorasib in Code Break 100, hepatotoxicity occurred in 1.7% (all grades) and 1.4%. (Grade 3). A total of 18% of patients who received Sotorasib had increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT)/increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST); 6% were Grade 3 and 0.6% were Grade 4. The median time to first onset of increased ALT/AST was 9 weeks (range: 0.3 to 42). Increased ALT/AST leading to dose interruption or reduction occurred in 7% of patients.
Sotorasib was discontinued due to increased ALT/AST in 2.0% of patients. In addition to dose interruption or reduction, 5% of patients received corticosteroids for the treatment of hepatotoxicity.
Monitor liver function tests (ALT, AST, and total bilirubin) prior to the start of Sotorasib, every 3 weeks for the first 3 months of treatment, then once a month or as clinically indicated, with more frequent testing in patients who develop transaminase and/or bilirubin elevations. Withhold, dose reduce or permanently discontinue Sotorasib based on severity of adverse reaction.
Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis
Sotorasib can cause ILD/pneumonitis that can be fatal. Among 357 patients who received Sotorasib in CodeBreaK 100, ILD/pneumonitis occurred in 0.8% of patients, all cases were Grade 3 or 4 at onset, and 1 case was fatal. The median time to first onset for ILD/pneumonitis was 2 weeks (range: 2 to 18 weeks).
Sotorasib was discontinued due to ILD/pneumonitis in 0.6% of patients. Monitor patients for new or worsening pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis (e.g., dyspnea, cough, fever). Immediately withhold Sotorasib in patients with suspected ILD/pneumonitis and permanently discontinue Sotorasib if no other potential causes of ILD/pneumonitis are identified.
SIDE EFFECTS
Two serious adverse effects were reported with the use of Sotorasib: hepatotoxicity and interstitial lung disease (ILD).
Hepatotoxicity:
Twenty-five percent of trial participants experienced liver dysfunction, resulting in elevated hepatic transami-nases, elevated bilirubin, and drug-induced hepatitis. Liver function tests should be performed before starting Sotorasib and every 3 weeks for the first 3 months, then once a month. Liver function tests should include AST, ALT, and bilirubin levels.2 Patients should be instructed to report signs or symptoms of liver dysfunction such as abdominal pain, jaundice, dark urine, or itching to their oncology team.
Sotorasib should be held if a patient develops grade 2, 3, or 4 hepatotoxicity until the symptoms resolve to a grade 1 or better, and then resumed at a lower dose.
Interstitial Lung Disease:
Although ILD was rare, several trial participants developed the condition. Patients should be evaluated regularly for respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath, cough, and fever, and should be encouraged to quickly report these symptoms to their healthcare team. If ILD is suspected, Sotorasib should be held while the patient undergoes work-up for their symptoms.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Effects of other medicinal products on Sotorasib
Acid-reducing agents
Coadministration of Sotorasib with gastric acid-reducing agents decreased Sotorasib concentrations, which may reduce the efficacy of Sotorasib. Avoid coadministration of Sotorasib with proton pump inhibitors (PP|s), H2 receptor antagonists, and locally acting antacids. If coadministration with an acid-reducing agent cannot be avoided, administer Sotorasib 4 hours before or 10 hours administration of a locally acting antacid. after
Strong CYP3A4 inducers
Coadministration of Sotorasib with a strong CYP3A4 inducer decreased Sotorasib concentrations, which may reduce the efficacy of Sotorasib. Avoid coadminis-tration of SOTORASIB with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
Effect of Sotorasib on other medicinal products
CYP3A4 substrates
Coadministration of Sotorasib with a CYP3A4 substrate decreased its plasma concentrations, which may reduce the efficacy of the substrate. Avoid coadministration of Sotorasib with CYP3A4 sensitive substrates, for which minimal concentration changes may lead to therapeutic failures of the substrate. If coadministration cannot be avoided, increase the sensitive CYP3A4 substrate dosage in accordance with its Prescribing Information.
P-glycoprotein (P-gp) Substrates
Coadministration of Sotorasib with a P-gp substrate (digoxin) increased digoxin plasma concentrations, which may increase the adverse reactions of digoxin. Avoid coadministration of Sotorasib with P-gp substrates, for which minimal concentration changes may lead to serious toxicities. If coadministration cannot be avoided, decrease the P-gp substrate dosage in accordance with its Prescribing Information.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATION
Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy
There are no data from the use of Sotorasib in pregnant women. Studies in animals have shown reproductive toxicity. Patients must be informed of the potential hazards to the foetus if Sotorasib is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking Sotorasib.
Breast-feeding
It is unknown if Sotorasib or its metabolites are excreted in human milk. A risk to newborns/infants cannot be excluded. A decision must be made whether to discontinue breast-feeding or to discontinue/abstain from Sotorasib therapy taking into account the benefit of breast feeding for the child and the benefit of therapy for the woman.
Fertility
There are no clinical studies to evaluate the effect of sotorasib on fertility.
OVERDOSE
There is no clinical experience with overdose with Sotorasib. In the event of an overdose, the patient should be treated symptomatically, and supportive measures instituted as required.
PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION
Storage Condition
Store below 25°C, in a cool and dry place. Keep away from light. Keep out of the reach of children.
HOW SUPPLIED
SOTOXEN tablet: Each HDPE container contains 56 film-coated tablets (each tablet contains 120 mg Sotorasib INN) a silica gel desiccant and polyester coil with a child-resistant closure.
Buy Generic Sotorasib Online
Are you interested to buy generic Sotorasib online? Don’t worry. 100 Meds can help you to find reliable and verified medicine at affordable cost. Please contact our support team by using email, whatsapp or wechat. Even you can contact our facebook page.
You must be logged in to post a review.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.